Ficheiro:Cooper pair box circuit.png
Cooper_pair_box_circuit.png (182 × 159 píxeis, tamanho: 2 kB, tipo MIME: image/png)
|
|
Esta imagem provém do Wikimedia Commons, um acervo de conteúdo livre da Wikimedia Foundation que pode ser utilizado por outros projetos.
|
Descrição do ficheiro
| DescriçãoCooper pair box circuit.png |
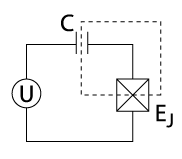
a Cooper-pair box (CPB). The system is almost the same as the single-electron box.there is an island to store charges, a bulk electrode to provide these charges, and a gate electrode to shift the electrostatic potential of the island with respect to the bulk electrode and to tune the number of charges thereby. The crucial difference is that now both the island and source electrodes are superconducting, and the tunnel junction that connects them is in fact a Josephson junction. There are two energies that characterize the system. The first energy is the Josephson energy of the junction.it is a periodic function of the superconducting phase difference across the junction,−EJcosϕ. It is convenient to set the phase of the lead to zero, so that the phase difference is just a phase that characterizes the superconducting state of the island. The second energy is the same as for the non-superconducting setup: the charging energy associated with discrete charge Ne in the island. Why is the system called a Cooperpairbox? Each superconductor is a coherent reservoir of Cooper pairs rather than electrons, provided the energies involved are smaller than the superconducting energy gap. In this section, we will assume that there is always an even number of extra elementary charges in the island, and that charges are always transferred in Cooper pairs. a Cooper-pair box (CPB). The system is almost the same as the single-electron box.there is an island to store charges, a bulk electrode to provide these charges, and a gate electrode to shift the electrostatic potential of the island with respect to the bulk electrode and to tune the number of charges thereby. The crucial difference is that now both the island and source electrodes are superconducting, and the tunnel junction that connects them is in fact a Josephson junction. There are two energies that characterize the system. The first energy is the Josephson energy of the junction.it is a periodic function of the superconducting phase difference across the junction,−EJcosϕ. It is convenient to set the phase of the lead to zero, so that the phase difference is just a phase that characterizes the superconducting state of the island. The second energy is the same as for the non-superconducting setup: the charging energy associated with discrete charge Ne in the island. Why is the system called a Cooperpairbox? Each superconductor is a coherent reservoir of Cooper pairs rather than electrons, provided the energies involved are smaller than the superconducting energy gap. In this section, we will assume that there is always an even number of extra elementary charges in the island, and that charges are always transferred in Cooper pairs. |
| Data | |
| Origem | Obra do próprio |
| Autor | Bjohnson00 (talk) (Uploads) |
Licenciamento
| A utilização deste ficheiro é regulada nos termos da licença Creative Commons - Atribuição-CompartilhaIgual 3.0 Não Adaptada. Sujeito a aviso legal (disclaimer). | ||
| Atribuição: Bjohnson00 em Wikipédia inglesa | ||
| ||
| Esta marca de licenciamento foi adicionada a este ficheiro durante a atualização da licença GFDL.http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/CC BY-SA 3.0Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0truetrue |

|
É concedida permissão para copiar, distribuir e/ou modificar este documento nos termos da Licença de Documentação Livre GNU, versão 1.2 ou qualquer versão posterior publicada pela Free Software Foundation; sem Secções Invariantes, sem textos de Capa e sem textos de Contra-Capa. É incluída uma cópia da licença na secção intitulada GNU Free Documentation License. Sujeito a aviso legal (disclaimer).http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
Registo de carregamento original
| Data e hora | Dimensões | Utilizador | Comentário |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005-12-16 18:09:37 | 182× 159× | Bjohnson00 | Author: Blake Johnson |

|
Esta imagem de um circuito (ou todas as imagens neste artigo ou categoria) deveriam ser recriadas usando gráficos vectoriais, como ficheiros SVG. Isto tem várias vantagens; veja as Commons:Media for cleanup|imagens para rever para mais informações. Se já criou um ficheiro SVG desta imagem, por favor, carregue-o. Depois do novo ficheiro SVG ter sido carregado, substitua aqui esta predefinição pela predefinição {{vector version available|nome da nova imagem.svg}}.
|
Legendas
Elementos retratados neste ficheiro
retrata
16 dezembro 2005
image/png
6dcdd5bcb4efcdc5a83d17b467dc2df58f12c454
2 115 byte
159 pixel
182 pixel
Histórico do ficheiro
Clique uma data e hora para ver o ficheiro tal como ele se encontrava nessa altura.
| Data e hora | Miniatura | Dimensões | Utilizador | Comentário | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| atual | 05h13min de 26 de dezembro de 2016 |  | 182 × 159 (2 kB) | FastilyClone | Transferred from en.wikipedia (MTC!) |
Utilização local do ficheiro
A seguinte página usa este ficheiro:
Utilização global do ficheiro
As seguintes wikis usam este ficheiro:
- ca.wikipedia.org
- en.wikipedia.org
Metadados
Este ficheiro contém informação adicional, provavelmente adicionada a partir da câmara digital ou scanner utilizada para criar ou digitalizar a imagem. Caso o ficheiro tenha sido modificado a partir do seu estado original, alguns detalhes poderão não refletir completamente as mudanças efetuadas.
| Software utilizado |
|
|---|